The reason for the warning light to show very often turns out to be a snapped belt which connects the alternator to the crankshaft. If it snaps, the cause of this failure should be determined first. If the problem is only the belt itself which was too old or, e.g., was damaged during incorrect installation, it is usually enough to replace the belt with a new one to remove the fault.
Burnt regulator and damaged diode plate
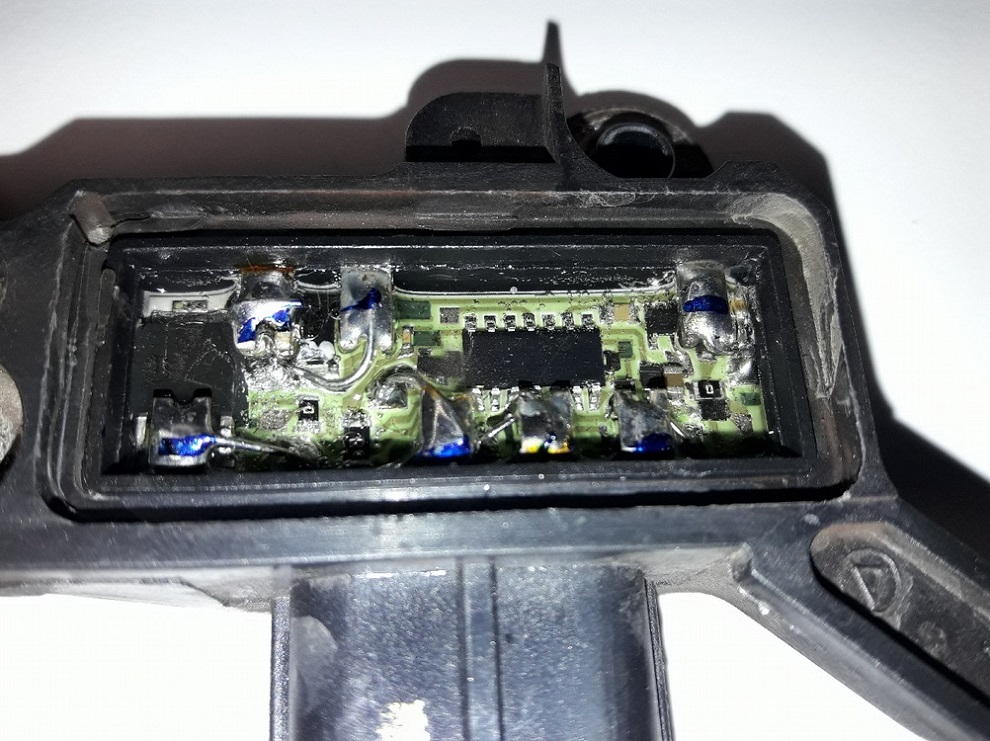

The faults of this component are most frequently caused by installation errors – often occurring during factory installation. The problem is the incorrect wiring of the battery. A sudden short circuit may lead to the destruction of the regulator and burning of the rectifier diodes.
Burnt voltage regulator
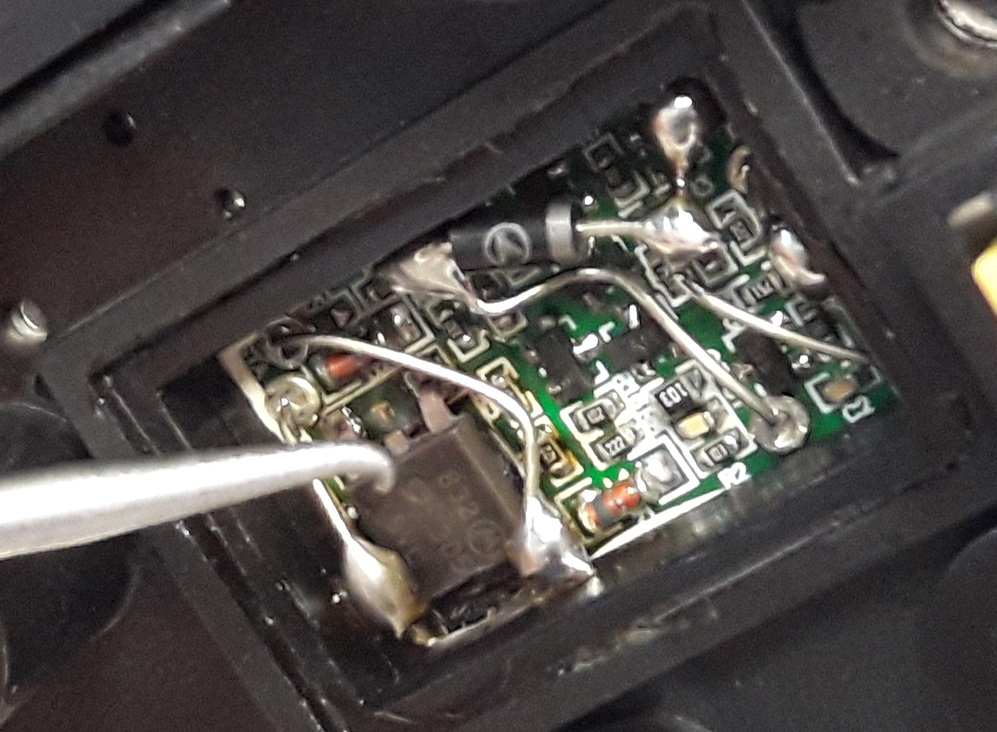

If the damage is limited to the regulator, and the diode plate remains intact, the probable cause of the fault is liquid ingress. The regulator might have been affected by water, oil or other operating fluid leaking from the pipes under the vehicle hood.
Burnt stator
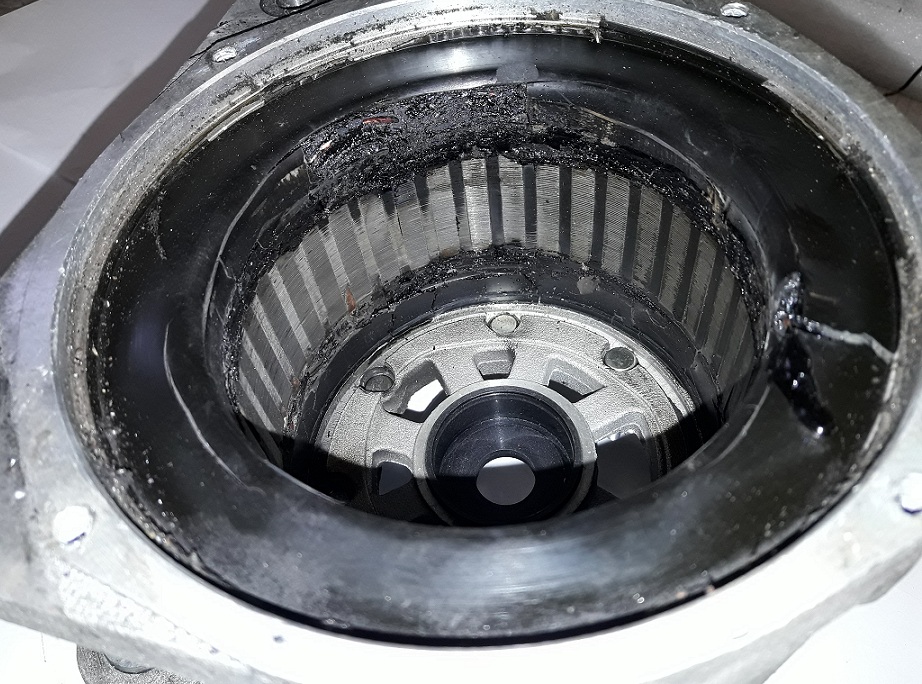

The reason for the stator burning is excessive alternator load which leads to its overheating. The excessive load might be a result of many reasons – intensive use of the vehicle devices (e.g. air supply), poor condition of the battery requiring constant recharging by the alternator or the normal wear and tear of the alternator.
Damaged rotor
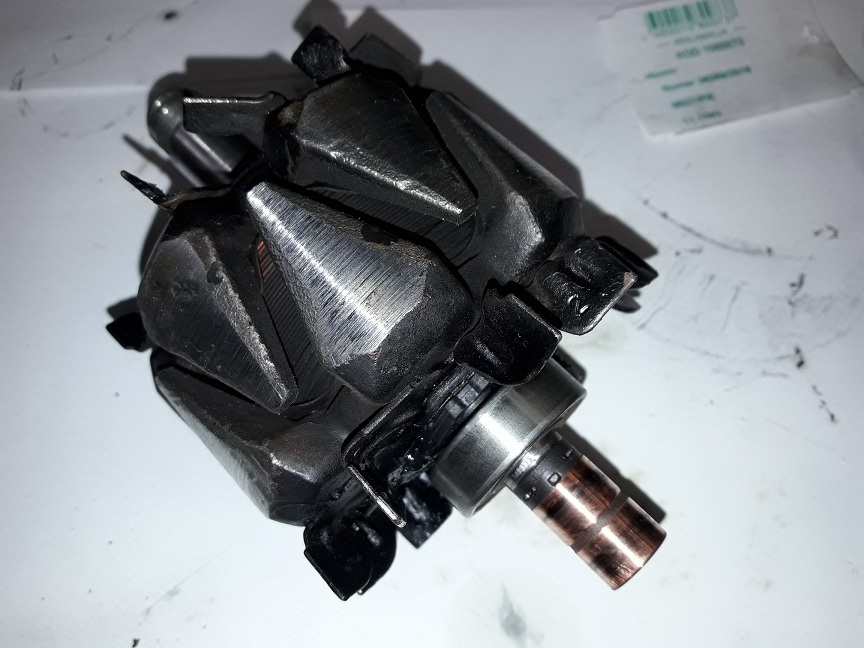

The current in the stator is generated by a rotor creating a magnetic field. The rotor is powered by mechanical energy from the crankshaft. Its failure is most commonly related to the normal wear and tear of the commutator which is the component responsible for current flow. The causes of failure may also include installation errors.
Worn bearings or pulley
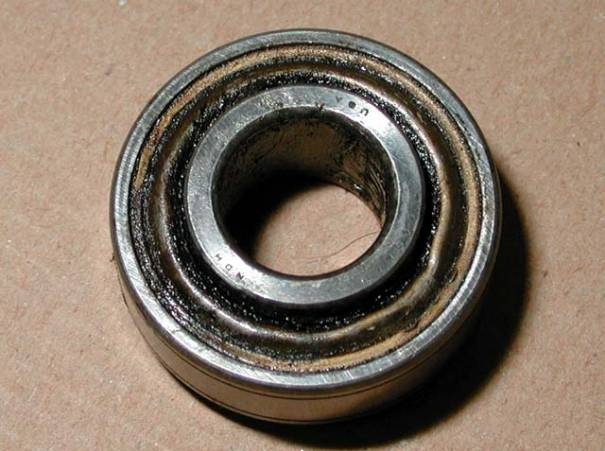

The alternator may also break down because of perfectly normal wear and tear of its parts. Premature wear of bearings is usually caused by the poor quality of materials used to produce them. It can also be affected by any external contaminants such as liquids or solids. The alternator pulley wears out over time. A particularly negative symptom is its uneven wear caused by, e.g., non-axial position of the poly-v belt (which is highly worn out or incorrectly installed).